AND OR NOT to Use Boolean Search Terms
One of the best ways to avoid those long lists of links when entering a list of keywords is to use Boolean logic operators. Each search engine will have their own way to enter logical operators. Be sure to look at the rules page at each site to learn how to use these words.
Boolean logical operators will either include or exclude items from a search. The following words are Boolean operators. Take a look at the example and the Venn diagrams that show what kind of results you can expect.
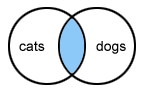
AND - Items found must have all the words linked by the word "and" in the search.
- for example: cats and dogs - displays only pages that have both words cats and dogs.
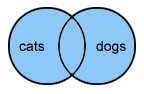
OR - Items found can have a single word or both words linked by the word "or" in the search.
- For example: cats or dogs - displays pages that either have both words cats and dogs, or only the word cats, or only the word dogs.
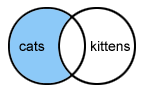
NOT - Items found cannot have the word linked by the word "not" in the search.
- For example: cats not kittens - displays pages that have the word cats without the word kittens.
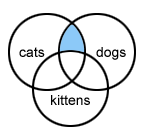
Using More Than One Operator
You can use more than one Boolean operator for more complex searches.
- For example: cats and dogs not kittens - displays pages that have both words cats and dogs, but do not have the word kittens.
Remember that Boolean searches are very specific. The word "kitten" and "kittens" are considered separate. If you want to eliminate both from your search, you need to include both words separated by the word "not."
- For example: cats and dogs not kittens not kitten
Some advanced search engines, like Google, have an advanced search page that builds these search terms in for you. On these pages, they may ask you to list words you don't want to see (NOT) in one area and all the words you would like to see (AND) in others.
Read more about: How to Find What You Need on the Internet
Bibliographic details:
- Article: Boolean Search Terms
- Author(s): Dr. Biology
- Publisher: Arizona State University School of Life Sciences Ask A Biologist
- Site name: ASU - Ask A Biologist
- Date published: 17 Dec, 2009
- Date accessed:
- Link: https://askabiologist.asu.edu/boolean-search-terms
APA Style
Dr. Biology. (Thu, 12/17/2009 - 15:43). Boolean Search Terms. ASU - Ask A Biologist. Retrieved from https://askabiologist.asu.edu/boolean-search-terms
Chicago Manual of Style
Dr. Biology. "Boolean Search Terms". ASU - Ask A Biologist. 17 Dec 2009. https://askabiologist.asu.edu/boolean-search-terms
Dr. Biology. "Boolean Search Terms". ASU - Ask A Biologist. 17 Dec 2009. ASU - Ask A Biologist, Web. https://askabiologist.asu.edu/boolean-search-terms
MLA 2017 Style
Be Part of
Ask A Biologist
By volunteering, or simply sending us feedback on the site. Scientists, teachers, writers, illustrators, and translators are all important to the program. If you are interested in helping with the website we have a Volunteers page to get the process started.



