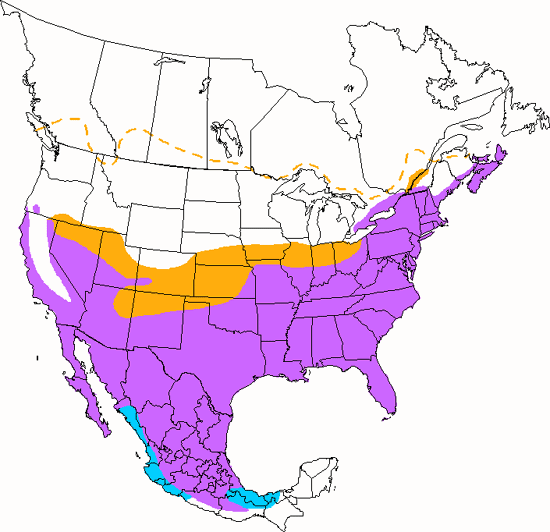
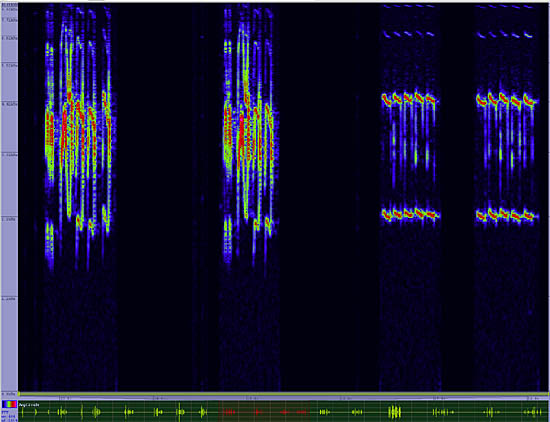
Northern Mockingbird
Mimus polyglottos

Perching

Length: 10 in. (25 cm )
Occurring in many types of open habitats, this species is as familiar in arid deserts as it is in suburbs and city centers. It is best known for its remarkable ability to mimic other birds\' songs as well as mechanical noises, such as whistles, cars and trains. The Mockingbird often flashes the big white patches in its wings and tail to intimidate rivals and cats. It aggressively defends its nest, even from unwary humans, by dive bombing perceived intruders. Unmated males sing all though the night in the Spring. It eats insects, invertebrates and fruits, and the nest is a cup-shaped construction placed in dense tangles or shrubbery.
The four-digit banding code is NOMO.
Bibliographic details:
- Article: Northern Mockingbird
- Author(s): Dr. Biology
- Publisher: Arizona State University School of Life Sciences Ask A Biologist
- Site name: ASU - Ask A Biologist
- Date published: 13 Jul, 2017
- Date accessed:
- Link: https://askabiologist.asu.edu/activities/bird/northern-mockingbird
APA Style
Dr. Biology. (Thu, 07/13/2017 - 15:37). Northern Mockingbird. ASU - Ask A Biologist. Retrieved from https://askabiologist.asu.edu/activities/bird/northern-mockingbird
Chicago Manual of Style
Dr. Biology. "Northern Mockingbird". ASU - Ask A Biologist. 13 Jul 2017. https://askabiologist.asu.edu/activities/bird/northern-mockingbird
Dr. Biology. "Northern Mockingbird". ASU - Ask A Biologist. 13 Jul 2017. ASU - Ask A Biologist, Web. https://askabiologist.asu.edu/activities/bird/northern-mockingbird
MLA 2017 Style
Be Part of
Ask A Biologist
By volunteering, or simply sending us feedback on the site. Scientists, teachers, writers, illustrators, and translators are all important to the program. If you are interested in helping with the website we have a Volunteers page to get the process started.