Horned Lark
Eremophila alpestris

Perching

Length: 7 in. (18 cm )
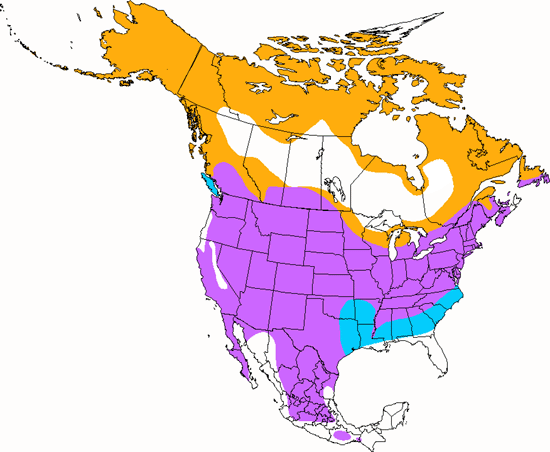
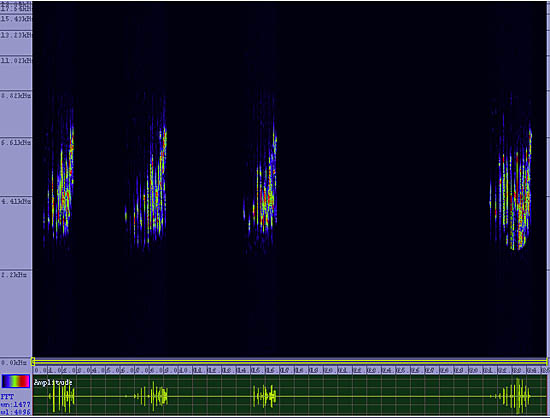
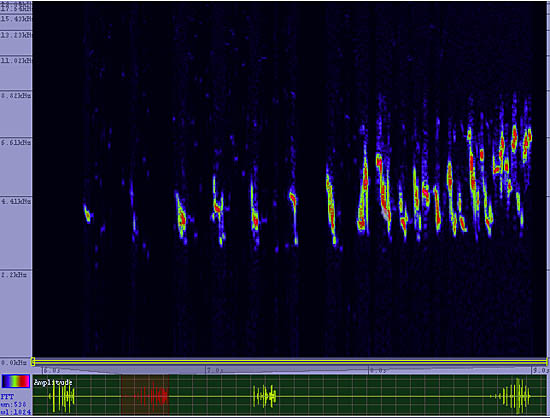
This ground bird thrives in extreme habitats such as plowed fields, beaches, airport runways and other barren areas that have few places to hide and no protection from cold winter storms. During the winter Horned Larks are inevitably in flocks, often with other open ground birds, where they run looking for seeds and then fly on to the next field in a tight flock trying to avoid marauding falcons and hawks. During the summer the flocks break up, and pairs nest in poorly vegetated fields, alpine areas and arctic tundra. They are so tough that even in northern states they are one of the first birds to start nesting - as early as February. They often sing while flying and fluttering high over head.
The four-digit banding code is HOLA.
Bibliographic details:
- Article: Horned Lark
- Author(s): Dr. Biology
- Publisher: Arizona State University School of Life Sciences Ask A Biologist
- Site name: ASU - Ask A Biologist
- Date published: 13 Jul, 2017
- Date accessed:
- Link: https://askabiologist.asu.edu/activities/bird/horned-lark
APA Style
Dr. Biology. (Thu, 07/13/2017 - 15:37). Horned Lark. ASU - Ask A Biologist. Retrieved from https://askabiologist.asu.edu/activities/bird/horned-lark
Chicago Manual of Style
Dr. Biology. "Horned Lark". ASU - Ask A Biologist. 13 Jul 2017. https://askabiologist.asu.edu/activities/bird/horned-lark
Dr. Biology. "Horned Lark". ASU - Ask A Biologist. 13 Jul 2017. ASU - Ask A Biologist, Web. https://askabiologist.asu.edu/activities/bird/horned-lark
MLA 2017 Style
Be Part of
Ask A Biologist
By volunteering, or simply sending us feedback on the site. Scientists, teachers, writers, illustrators, and translators are all important to the program. If you are interested in helping with the website we have a Volunteers page to get the process started.